PROCEDURE
1. Simulation for finding load current by direct method
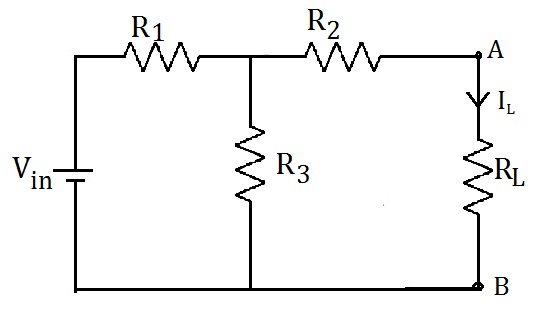
(i) Keep switch S1 to position 1 (Input supply is fed).
(ii) Keep switch S2 to position 2 (Load is connected).
(iii) Run the simulation and note down the current through load resistor from ammeter reading.
(iv) Click Next.
2. Simulation for finding Thevenin Voltage
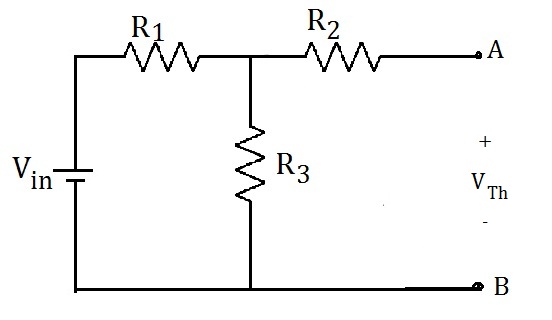
(i) Keep switch S1 to position 1 (Input supply is fed).
(ii) Keep switch S2 to position 2 (Open).
(iii) Run the simulation and note down the voltage across the reading, which will give Norton equivalent current (INorton).
(iv) Click Next.
3. Simulation for finding Norton Equivalent Resistance
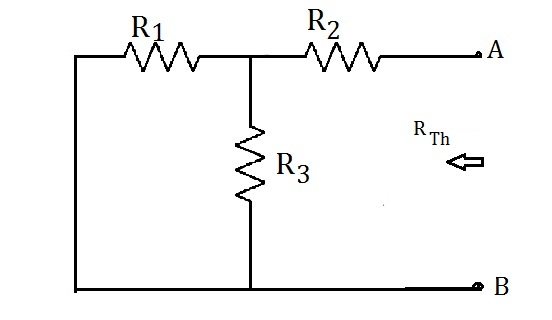
(i) Keep switch S1 to position 2 (Input voltage source is shorted).
(ii) Keep switch S2 to position 1 (Supply is given to measure resistance by ammeter - voltmeter method).
(iii) Run the simulation and note down the voltage (Voltmeter reading) ,
current (Ammeter reading) and Norton Equivalent resistance(RNorton=V/I) .
(iv) Click Next.
4. Simulation for finding Load current from Norton equivalent circuit
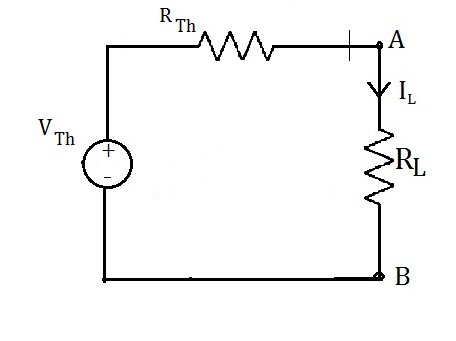
(i) Ensure the Norton equivalent circuit current source is having the value
same as the Norton equivalent current and resistance same that of Norton Equivalent resistance.
(ii) Run the simulation and note down the load current from Norton equivalent circuit.
5. From the updated observation table, note down actual load current obtained from step 1 (First column) and load current obtained using Norton equivalent circuit from step 4 (8th Column) are equal and hence Norton theorem is verified.
6. Click Finish.
7. Repeat the experiment by changing circuit components and complete observation table.



