Menu
THEORY
Thevenin’s Theorem states that “Any linear circuit containing several voltages and resistances can be replaced by just one single voltage in series with a single resistance connected across the load“.
In other words, it is possible to simplify any electrical circuit, no matter how complex, to an equivalent two-terminal circuit with just a single constant voltage source in series with a resistance connected to a load.
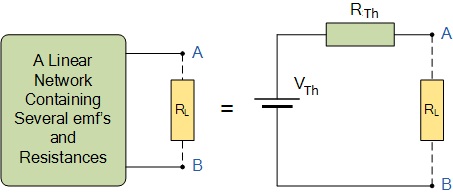
As far as the load resistor RL is concerned, any complex “one-port” network consisting of multiple resistive circuit elements and energy sources can be replaced by one single equivalent resistance RTh and one single equivalent voltage VTh. RThis the source resistance value looking back into the circuit and VTh is the open circuit voltage at the terminals.
The basic procedure for solving a circuit using Thevenin’s Theorem is as follows: